Finite State Machine is a mathematical model of computation that models a sequential logic. FSM consists of a finite number of states, transition functions, input alphabets, a start state and end state(s). In the field of computer science, the FSMs are used in designing Compilers, Linguistics Processing, Step workflows, Game Design, Protocols Procedures (like TCP/IP), Event-driven programming, Conversational AI and many more.
To understand what a finite machine is, we take a look at Traffic Signal. Finite State Machine for a Traffic Signal is designed and rendered below. Green is the start/initial state, which upon receiving a trigger moves to Yellow, which, in turn, upon receiving a trigger, transitions to Red. The Red then circles back to Green and the loop continues.

An FSM must be in exactly one of the finite states at any given point in time and then in response to an input, it receives, the machine transitions to another state. In the example above, the traffic signal is exactly in one of the 3 states - Green, Yellow or Red. The transition rules are defined for each state which defines what sequential logic will be played out upon input.
Implementing an FSM is crucial to solving some of the most interesting problems in Computer Science and in this article, we dive deep into modeling a Finite State Machine using Python coroutines.
Python Coroutines
Before diving into the implementation we take a detour and look at what Generators and Coroutines are, how they keep implementation intuitive and fits into the scheme of things.
Generators
Generators are resumable functions that yield values as long as someone, by calling next function, keeps asking it. If there are no more values to yield, the generator raises a StopIteration exception.
def fib():
a, b = 0, 1
while True:
yield a
a, b = b, a+b
The yield statement is where the magic happens. Upon reaching the yield statement, the generator function execution is paused and the yielded value is returned to the caller and the caller continues its execution. The flow returns back to the generator when the caller function asks from the next value. Once the next value is requested by calling next (explicitly or implicitly), the generator function resumes from where it left off i.e. yield statement.
>>> fgen = fib()
>>> [next(fgen) for _ in range(10)]
[0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, 34]
Using a Fibonacci generator is memory-efficient as now we need not compute a lot of Fibonacci numbers and hold them in memory, in a list, rather the requesting process could ask for as many values as it needs and the generator would keep on yielding values one by one.
Coroutines
Coroutines, just like generators, are resumable functions but instead of generating values, they consume values on the fly. The working of it is very similar to the generator and again the yield statement is where the magic happens. When a coroutine is paused at the yield statement, we could send the value it using send function and the value could be used using the assignment operator = on yield as shown below
def grep(substr):
while True:
line = yield
if substr in line:
print(f"found {substr}")
In the example above, we wrote a simple grep utility that checks for a substring in a given stream of text. When the coroutine grep is paused at the yield statement, using the send function, we send the text to it, and it will be referenced by the variable line. The coroutine then continues its execution to check if substr is in line or not. Once the flow reaches the yield statement again, the coroutine pauses and waits for the caller to send it a new value.
Note that, this is not a thread that keeps on running and hogging the CPU. It is just a function whose execution is paused at the yield statement waiting for the value; the state is persisted and the control is passed back to the caller. When resumed the coroutine starts from the same state where it left off.
Before sending the value to a coroutine we need to "prime" it so that the flow reaches the yield statement and the execution is paused while waiting for the value to be sent.
>>> g = grep("users/created")
>>> next(g) # priming the generator
>>>
>>> g.send("users/get api took 1 ms.")
>>> g.send("users/created api took 3 ms.")
found users/created
>>> g.send("users/get api took 1 ms.")
>>> g.send("users/created api took 4 ms.")
found users/created
>>> g.send("users/get api took 1 ms.")
In the function invocations above we see how we could keep on sending the text to the coroutine and it continues to spit out if it found the given substring users/created in the text. This ability of coroutine to pause the execution and accept input on the fly helps us model FSM in a very intuitive way.
Building a Finite State Machine
While building FSMs, the most important thing is how we decide to model and implement states and transition functions. States could be modeled as Python Coroutines that run an infinite loop within which they accept the input, decides the transition and updates the current state of the FSM. The transition function could be as simple as a bunch of if and elif statements and in a more complex system it could be a decision function.
To dive into low-level details, we build an FSM for the regular expression ab*c, which means if the given string matches the regex then the machine should end at the end state, only then we say that the string matches the regex.

State
From the FSM above we model the state q2 as
def _create_q2():
while True:
# Wait till the input is received.
# once received store the input in `char`
char = yield
# depending on what we received as the input
# change the current state of the fsm
if char == 'b':
# on receiving `b` the state moves to `q2`
current_state = q2
elif char == 'c':
# on receiving `c` the state moves to `q3`
current_state = q3
else:
# on receiving any other input, break the loop
# so that next time when someone sends any input to
# the coroutine it raises StopIteration
break
The coroutine runs as an infinite loop in which it waits for the input token at the yield statement. Upon receiving the input, say b it changes the current state of FSM to q2 and on receiving c changes the state to q3 and this precisely what we see in the FSM diagram.
FSM Class
To keep things encapsulated we will define a class for FSM which holds all the states and maintains the current state of the machine. It will also have a method called send which reroutes the received input to the current state. The current state upon receiving this input makes a decision and updates the current_state of the FSM as shown above.
Depending on the use-case the FSM could also have a function that answers the core problem statement, for example, does the given line matches the regular expression? or is the number divisible by 3?
The FSM class for the regular expression ab*c could be modeled as
class FSM:
def __init__(self):
# initializing states
self.start = self._create_start()
self.q1 = self._create_q1()
self.q2 = self._create_q2()
self.q3 = self._create_q3()
# setting current state of the system
self.current_state = self.start
# stopped flag to denote that iteration is stopped due to bad
# input against which transition was not defined.
self.stopped = False
def send(self, char):
"""The function sends the curretn input to the current state
It captures the StopIteration exception and marks the stopped flag.
"""
try:
self.current_state.send(char)
except StopIteration:
self.stopped = True
def does_match(self):
"""The function at any point in time returns if till the current input
the string matches the given regular expression.
It does so by comparing the current state with the end state `q3`.
It also checks for `stopped` flag which sees that due to bad input the iteration of FSM had to be stopped.
"""
if self.stopped:
return False
return self.current_state == self.q3
...
@prime
def _create_q2(self):
while True:
# Wait till the input is received.
# once received store the input in `char`
char = yield
# depending on what we received as the input
# change the current state of the fsm
if char == 'b':
# on receiving `b` the state moves to `q2`
self.current_state = self.q2
elif char == 'c':
# on receiving `c` the state moves to `q3`
self.current_state = self.q3
else:
# on receiving any other input, break the loop
# so that next time when someone sends any input to
# the coroutine it raises StopIteration
break
...
Similar to how we have defined the function _create_q2 we could define functions for the other three states start, q1 and q3. You can find the complete FSM modeled at arpitbbhayani/fsm/regex-1
Driver function
The motive of this problem statement is to define a function called grep_regex which tests a given text against the regex ab*c. The function will internally create an instance of FSM and will pass the stream of characters to it. Once all the characters are exhausted, we invoke does_match function on the FSM which suggests if the given text matches the regex ab*c or not.
def grep_regex(text):
evaluator = FSM()
for ch in text:
evaluator.send(ch)
return evaluator.does_match()
>>> grep_regex("abc")
True
>>> grep_regex("aba")
False
The entire execution is purely running sequential - and that's because of Coroutines. All states seem to run in parallel but they that are all executing in one thread concurrently. The coroutine of the current state is executing while all others are suspended on their corresponding
yieldstatements. When a new input is sent to the coroutine it is unblocked completes its execution, changes the current state of FSM and pauses itself on itsyieldstatement again.
More FSMs
We have seen how intuitive it is to build Regular expression FSMs using Python Coroutines, but if our hypothesis is true things should equally intuitive when we are implementing FSMs for other use cases and here we take a look at two examples and see how a state is implemented in each
Divisibility by 3
Here we build an FSM that tells if a given stream of digits of a number is divisible by 3 or not. The state machine is as shown below.

We can implement the state q1 as a coroutine as
def _create_q1(self):
while True:
digit = yield
if digit in [0, 3, 6, 9]:
self.current_state = self.q1
elif digit in [1, 4, 7]:
self.current_state = self.q2
elif digit in [2, 5, 8]:
self.current_state = self.q0
We can see the similarity between the coroutine implementation and the transition function for a state. The entire implementation of this FSM can be found at arpitbbhayani/fsm/divisibility-by-3.
SQL Query Validator
Here we build an FSM for a SQL Query Validator, which for a given a SQL query tells if it is a valid SQL query or not. The FSM for the validator that covers all the SQL queries will be massive, hence we just deal with the subset of it where we support the following SQL queries
SELECT * from TABLE_NAME;
SELECT column, [...columns] from TABLE_NAME;
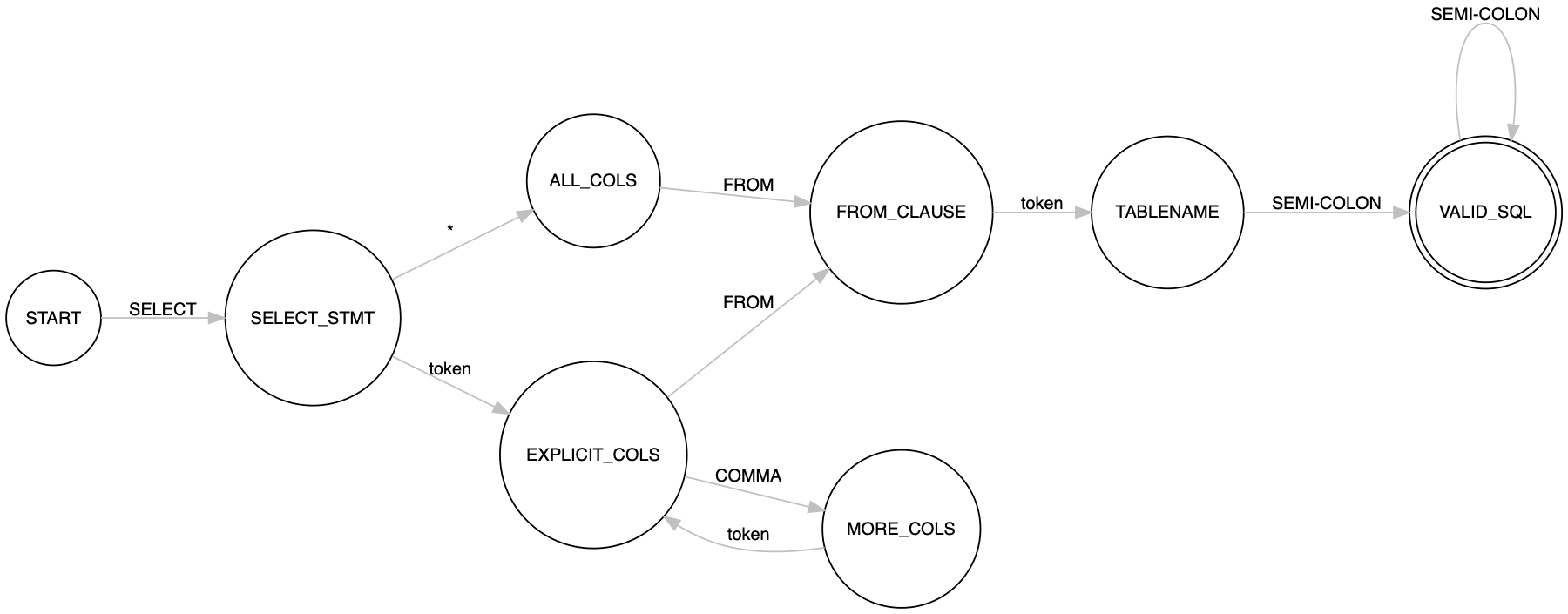
We can implement the state explicit_cols as a coroutine as
def _create_explicit_cols(self):
while True:
token = yield
if token == 'from':
self.current_state = self.from_clause
elif token == ',':
self.current_state = self.more_cols
else:
break
Again the coroutine through which the state is implemented is very similar to the transition function of the state keeping things intuitive. The entire implementation of this FSM can be found at arpitbbhayani/fsm/sql-query-validator.
Conclusion
Even though this may not be the most efficient way to implement and build FSM but it is the most intuitive way indeed. The edges and state transitions, translate well into if and elif statements or the decision functions, while each state is being modeled as an independent coroutine and we still do things in a sequential manner. The entire execution is like a relay race where the baton of execution is being passed from one coroutine to another.
